What Are Enterprise Sales Solutions and Why Do They Matter in 2026?

What Are Enterprise Sales Solutions and Why Do They Matter in 2026?
Enterprise sales solutions are unified platforms that help B2B sales teams manage complex, high-value deals across multiple stakeholders, departments, and long sales cycles. In 2026, these tools have evolved from simple CRMs into AI-powered revenue engines that consolidate prospecting, engagement, analytics, and deal execution into one workspace.
According to a 2025 B2B AI report, 100% of sales enablement leaders now use generative AI, up from just 62% in 2024. This shift reflects a fundamental change: enterprise sales solutions are no longer optional. They're the backbone of competitive revenue operations.
Apollo Delivers 96% Email Accuracy Instantly
Tired of bounced emails and disconnected numbers? Apollo verifies 224M+ contacts in real-time so your team connects with decision-makers, not dead ends. Join 550K+ companies closing more deals with accurate data.
Start Free with Apollo →Key Takeaways
- Enterprise sales solutions unify prospecting, engagement, and deal management in one platform, cutting tech stack costs by 50% or more
- AI-driven features like conversation intelligence and predictive forecasting have become standard, with 48% of organizations reporting direct revenue increases
- Modern platforms prioritize data quality and enrichment, with leading solutions offering 96% email accuracy across 224M+ contacts
- Integration capabilities and workflow automation are now table stakes for enterprise adoption
- The shift from tool sprawl to consolidated platforms accelerates sales cycles by 51% on average
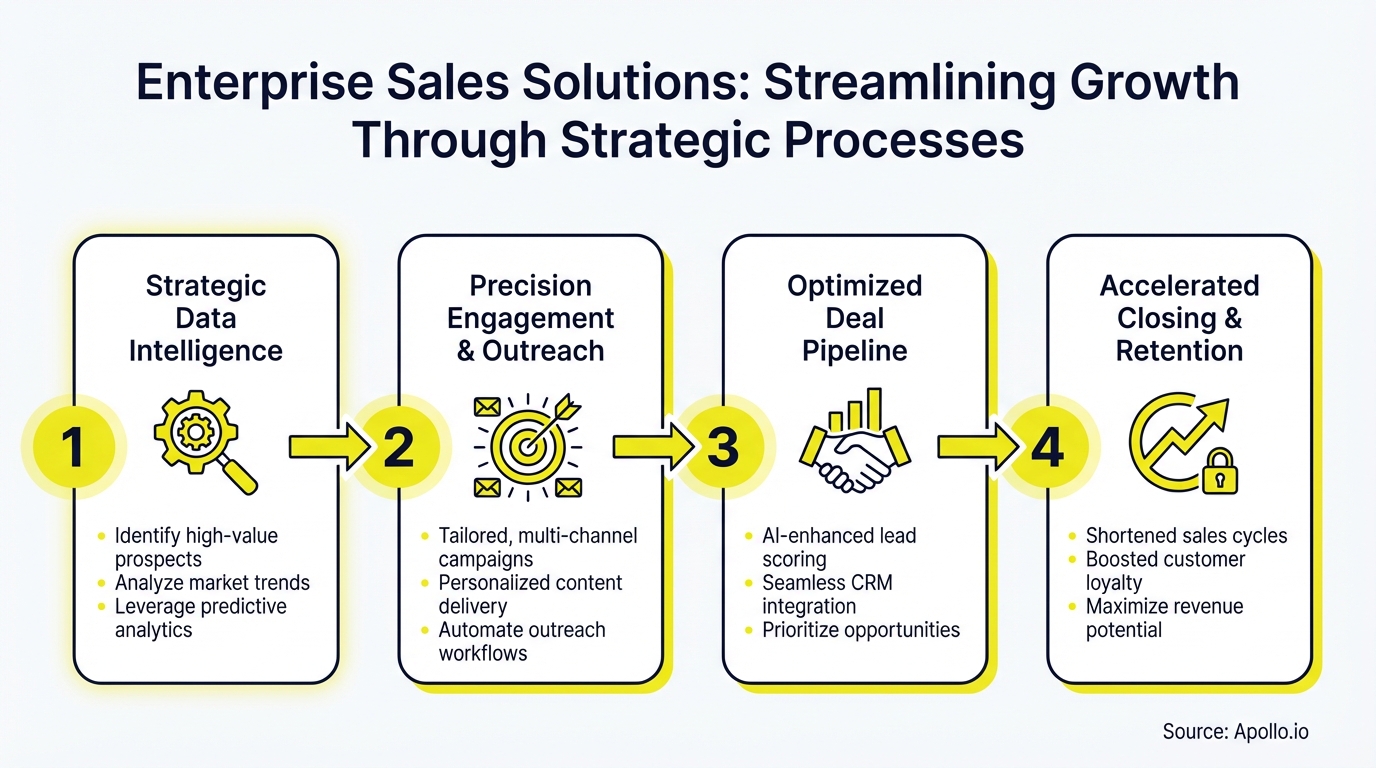
What Defines Enterprise Sales Solutions in 2026?
Enterprise sales solutions are platforms designed for organizations selling complex products or services with deal values typically exceeding $50K. These solutions differ from SMB tools in three critical ways:
Scale and Complexity: Enterprise solutions handle hundreds or thousands of users, multi-threaded account hierarchies, and intricate approval workflows. They manage territory assignments, quota tracking, and revenue forecasting across global teams.
Data Intelligence: Modern enterprise platforms provide deep buyer intelligence, including technographic data, intent signals, and org chart mapping. Research by McKinsey shows 64% of B2B companies increased predictive analytics investments in 2024, recognizing data as their competitive edge.
Integration Architecture: Enterprise solutions integrate with existing tech stacks (ERP, marketing automation, customer success platforms) while maintaining data integrity across systems.
"Apollo could be a third of the cost if you look at the full price of what we were spending on ZoomInfo, Outreach, Salesforce, and admins to make it all work."
Why Do Enterprise Teams Need Specialized Sales Solutions?
Enterprise sales cycles involve 6-10 stakeholders, span 6-18 months, and require coordinated outreach across multiple channels. Generic tools can't handle this complexity.
Managing Multi-Threaded Accounts: Enterprise deals require mapping decision-makers, influencers, and champions across departments. Solutions must track relationships, communication history, and buying signals for each stakeholder.
Accelerating Long Sales Cycles: Time kills deals. Enterprise solutions automate follow-ups, surface engagement signals, and alert reps when prospects show buying intent. Data from the 2025 B2B AI adoption study shows 51% of organizations shortened sales cycles through AI implementation.
Aligning Cross-Functional Teams: Sales, marketing, customer success, and product teams need shared visibility into account status, engagement history, and revenue forecasts. Struggling with disconnected tools and data silos? Unify your revenue operations with Apollo's deal management platform.
"Having Apollo and having everything be in one system was a game changer — for BDRs specifically."
What Are the Must-Have Features of Enterprise Sales Solutions?
| Feature Category | Core Capabilities | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Prospecting & Data | 224M+ verified contacts, 65+ filters, technographic data, intent signals | Reduce research time from hours to minutes |
| Sales Engagement | Multi-channel sequences, A/B testing, AI personalization, dialer integration | Increase meeting bookings by 75% |
| AI & Automation | Conversation intelligence, email generation, predictive scoring, workflow triggers | 10x personalized outreach capacity |
| Analytics & Forecasting | Pipeline visibility, win/loss analysis, rep performance dashboards, revenue predictions | Improve forecast accuracy by 30% |
| Integrations | Native CRM sync, API access, webhook automation, data enrichment | Eliminate manual data entry |
Advanced Account Mapping: Visualize org charts, identify decision-makers, and track relationship strength across accounts. Modern platforms use AI to suggest which contacts to engage based on title, seniority, and engagement history.
Deal Management & Pipeline Tracking: Monitor deal progress, identify at-risk opportunities, and forecast revenue with confidence. Solutions should provide real-time visibility into deal status, next steps, and blockers. Learn more about streamlining your sales pipeline.
AI-Powered Insights: Modern platforms analyze call recordings, email exchanges, and engagement patterns to surface winning behaviors and coach reps in real-time. The 2025 B2B AI report found 81% of enablement teams now use AI for sales content creation.

How Do Enterprise Sales Solutions Drive Revenue Growth?
The ROI of enterprise sales solutions extends beyond efficiency gains. Organizations report three primary revenue impacts:
Faster Time-to-Revenue: New reps reach quota 44% faster with AI-assisted onboarding and built-in playbooks. Sales cycles shorten when teams have instant access to verified contact data and engagement insights.
Higher Win Rates: Organizations using unified platforms see 30-50% higher win rates on enterprise deals. Consolidated data eliminates information gaps that cause deals to stall.
Increased Deal Sizes: Account mapping features help teams identify expansion opportunities and cross-sell into additional departments. Teams using AI sales tools report 46% more meetings booked and 35% increases in bookings.
Wasting hours on manual prospecting and outdated contact data? Access Apollo's 224M+ verified contacts with 96% email accuracy.
What Are the Implementation Pitfalls to Avoid?
Tool Sprawl vs. Consolidation: Many enterprises still juggle 5-10 sales tools (prospecting database, engagement platform, dialer, analytics, CRM). This creates data silos, integration headaches, and vendor fatigue. The winning strategy in 2026 is platform consolidation.
Data Quality Issues: Enterprise solutions are only as good as their data. Platforms with built-in enrichment and verification (96% email accuracy or higher) eliminate the need for separate data vendors.
Low User Adoption: Complex interfaces and steep learning curves kill ROI. Choose solutions with intuitive UX, Chrome extensions for inline prospecting, and mobile apps for on-the-go access.
Integration Complexity: Ensure your solution offers native CRM integrations, robust APIs, and pre-built connectors to your existing tech stack. Explore strategic sales development approaches for implementation best practices.
Replace Forecast Guesswork With Real Visibility
Pipeline forecasting feel like throwing darts blindfolded? Apollo gives you real-time deal stage visibility and intent signals so you actually know what's closing. Built-In increased win rates 10% with Apollo's scoring.
Start Free with Apollo →What Trends Are Shaping Enterprise Sales Solutions?
AI-Native Architectures: Every major platform now embeds AI for research, personalization, forecasting, and coaching. The question isn't whether to adopt AI, but how deeply it's integrated into daily workflows.
Revenue Operations Alignment: Modern solutions blur the lines between sales, marketing, and customer success. Unified platforms provide shared metrics, account views, and handoff workflows across the revenue team.
Conversational Intelligence: Call and email analysis is now standard. Leading platforms transcribe calls, extract action items, identify objections, and coach reps on winning talk tracks. Check out AI call assistant tools for conversation intelligence.
Composable Tech Stacks: While consolidation is the trend, enterprises still need flexibility. API-first architectures let teams build custom workflows while maintaining a unified data layer.
How to Choose the Right Enterprise Sales Solution
Start with a needs assessment: What are your biggest sales bottlenecks? Where do reps spend time on low-value tasks? Which processes break down as deals move through your pipeline?
Evaluate solutions on five criteria: (1) Data quality and coverage, (2) Engagement automation capabilities, (3) AI features and roadmap, (4) Integration ecosystem, and (5) Total cost of ownership including implementation and training.
Run a proof-of-concept with 10-20 reps before rolling out enterprise-wide. Measure specific KPIs like time-to-first-meeting, email response rates, and pipeline velocity. Understand B2B sales strategies and metrics to set benchmarks.
Consider total cost of consolidation. Many organizations cut sales tech spending by 50% when moving from 5+ tools to one unified platform.
Take Action: Modernize Your Enterprise Sales Stack
Enterprise sales solutions have evolved from nice-to-have tools into strategic revenue drivers. The data is clear: organizations with unified, AI-powered platforms close deals faster, win at higher rates, and operate more efficiently than those stuck with tool sprawl.
The shift to consolidated platforms isn't just about cost savings. It's about giving reps a single source of truth, eliminating context switching, and leveraging AI to focus human effort on high-value activities.
As 80% of B2B sales interactions move to digital channels, your platform choice will determine whether you're leading or lagging in your market.
Ready to see how a unified platform accelerates your enterprise sales motion? Start your free Apollo trial and experience 224M+ verified contacts, AI-powered engagement, and deal management in one workspace.
Prove Apollo's ROI In Your First 30 Days
Budget approval stuck on unclear metrics? Apollo tracks every touchpoint from first contact to closed deal, showing exactly what's working. Built-In increased win rates 10% and ACV 10% with Apollo's scoring.
Start Free with Apollo →Don't miss these
Sales
Inbound vs Outbound Marketing: Which Strategy Wins?
Sales
What Is a Sales Funnel? The Non-Linear Revenue Framework for 2026
Sales
What Is a Go-to-Market Strategy? The Data-Driven Blueprint That Actually Works
See Apollo in action
We'd love to show how Apollo can help you sell better.
By submitting this form, you will receive information, tips, and promotions from Apollo. To learn more, see our Privacy Statement.
4.7/5 based on 9,015 reviews
