How Does B2B Software Integration Drive Revenue in 2026?

How Does B2B Software Integration Drive Revenue in 2026?
B2B software integration is no longer optional. Your CRM, marketing automation, ERP, and sales engagement tools must communicate seamlessly or you're leaving revenue on the table. According to Gartner's 2024 iPaaS market analysis, the integration platform as a service market grew 23.4% to $8.5 billion, signaling that companies are consolidating tools and demanding unified workflows.
The challenge: most B2B teams juggle 5-10 disconnected tools, resulting in duplicate data entry, missed handoffs, and lost deals. The solution: an architecture-first approach to integration that prioritizes data quality, AI capabilities, and ROI measurement.
Scale Quality Leads Without Adding Headcount
Struggling with slow lead generation while your team hits capacity? Apollo automates prospect research and qualification at scale. Customer. io grew 50% YoY with streamlined workflows.
Start Free with Apollo →Key Takeaways
- B2B software integration eliminates data silos and reduces manual work across CRM, ERP, and marketing platforms
- AI-powered integration platforms (iPaaS) now handle intelligent data mapping, anomaly detection, and automated workflows
- The iPaaS market grew 23.4% in 2024, while the broader integration software market reached $34.8 billion
- Successful integration requires governance frameworks, security protocols, and measurable ROI tracking
- Unified platforms like Apollo consolidate prospecting, enrichment, and engagement in one workspace, cutting tech stack costs
What Is B2B Software Integration and Why It Matters Now
B2B software integration connects disparate business applications so data flows automatically between systems. This includes CRM-to-marketing automation, ERP-to-sales engagement, and data enrichment-to-pipeline management connections.
The business case is clear. Research by Gartner shows integration software technologies grew 10.9% in 2024 to $34.8 billion. Companies are investing because fragmented systems create revenue-killing friction: sales reps waste hours on data entry, marketing can't track attribution, and leadership lacks real-time pipeline visibility.
Modern B2B sales organizations need integration to support multi-channel outreach, AI-driven personalization, and data-backed decision making. Without it, your tech stack becomes a liability instead of an asset.
The Architecture of Modern B2B Integration
Effective B2B software integration follows proven architectural patterns. Here are the core approaches:
| Integration Pattern | Best For | Complexity | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point | 2-3 systems | Low | CRM to email platform |
| Hub-and-Spoke (iPaaS) | 5+ systems | Medium | Central data warehouse feeding multiple tools |
| Event-Driven | Real-time workflows | High | Instant lead routing from form submission to rep assignment |
| API-First Platform | Custom integrations | Medium-High | Building proprietary sales intelligence workflows |
Most growing B2B companies adopt a hub-and-spoke model using iPaaS solutions. This centralizes data governance, reduces point-to-point integration sprawl, and enables AI-powered data orchestration.
"Apollo enriches everything we have: contacts, leads, accounts... And we don't really have to touch it, it just works."

How AI-Powered Integration Changes the Game
AI is transforming B2B software integration from simple data transfer to intelligent orchestration. Modern platforms now offer:
- Intelligent Data Mapping: AI automatically identifies matching fields across systems (e.g., "Company Name" vs "Account Name" vs "Organization")
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning flags data quality issues, duplicate records, and suspicious patterns before they corrupt your database
- Predictive Routing: AI determines optimal lead assignment based on rep performance, industry expertise, and current workload
- Auto-Enrichment: Systems proactively fill missing contact data, update job changes, and append firmographic details
These capabilities directly impact revenue. When your CRM integration strategy includes AI-powered enrichment, sales reps spend less time researching and more time selling. When intelligent routing connects to your lead scoring software, high-intent prospects reach the right rep immediately.
Struggling to keep contact data clean across systems? Apollo enriches 224M+ contacts automatically with 96% email accuracy.
Evaluating B2B Integration Platforms: What to Prioritize
Selecting the right integration approach requires balancing capabilities, cost, and complexity. Use this framework:
| Evaluation Criteria | Questions to Ask | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Built Connectors | Does it support our core stack (CRM, MAP, ERP, sales engagement)? | Requires custom dev for common integrations |
| Data Governance | Can we control data flow, set permissions, and audit changes? | No role-based access or change logs |
| AI Capabilities | Does it offer smart mapping, enrichment, and anomaly detection? | Manual field mapping only |
| Real-Time vs. Batch | Do we need instant updates or can we sync hourly/daily? | Batch-only for time-sensitive workflows |
| Total Cost of Ownership | What's the all-in cost including licenses, dev time, and maintenance? | Hidden fees for API calls or data volume |
The most successful teams evaluate integration as part of their broader B2B marketing tools strategy, not as a standalone IT project. Integration should reduce your tech stack footprint, not expand it.
"We benchmarked ZoomInfo versus Apollo, Clearbit, Lusha, and Seamless, and ultimately Apollo won on all fronts, especially in enrichment. Higher quality than ZoomInfo, greater breadth than Clearbit."
See Every Deal Stage In Real Time With Apollo
Pipeline forecasting a guessing game? Apollo gives you live visibility into every deal stage so you can forecast with confidence. Built-In boosted win rates 10% with Apollo's scoring.
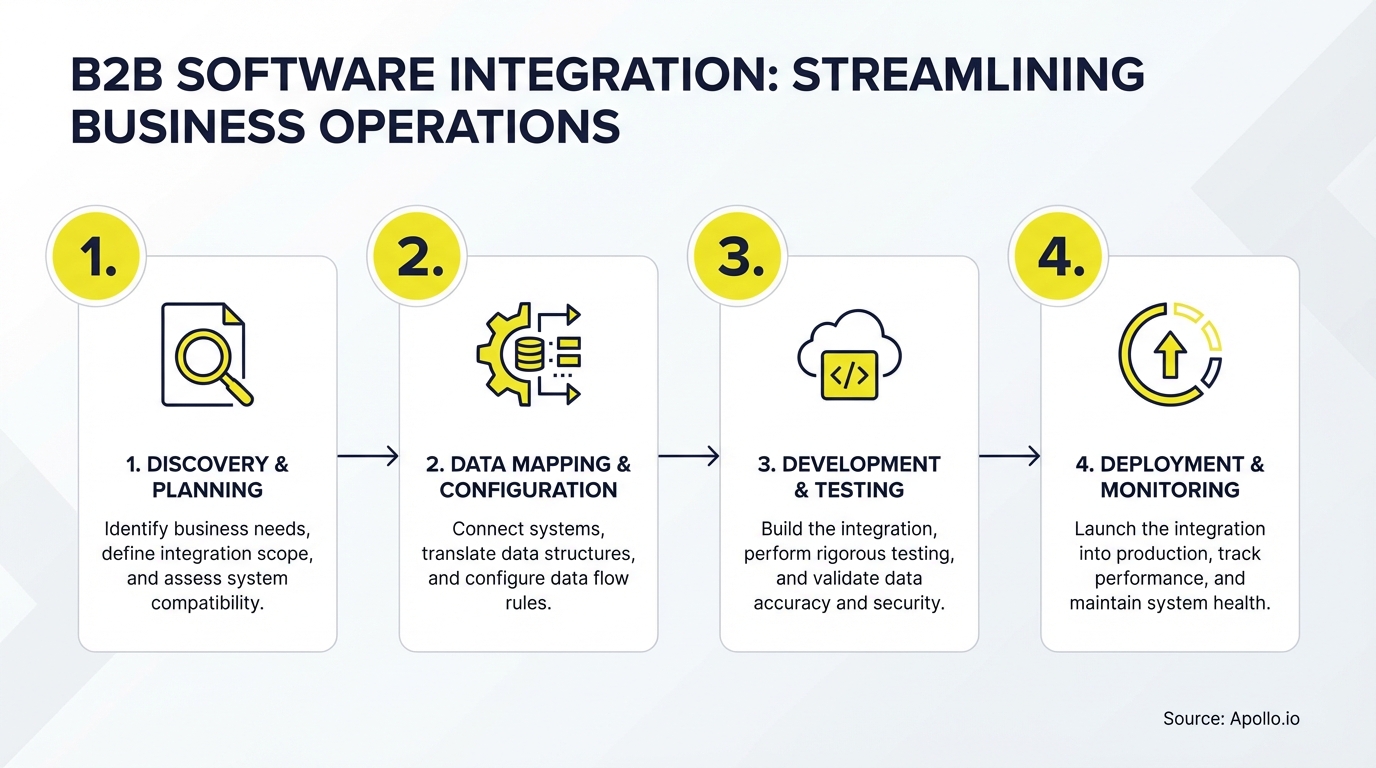
Start Free with Apollo →Implementation Playbook: From Planning to Production
Successful B2B software integration follows a structured rollout process:
- Audit Current State: Map all existing tools, data flows, and integration points. Identify duplicate systems and manual handoffs.
- Define Integration Architecture: Choose your pattern (point-to-point, iPaaS, API-first). Document data governance rules and security requirements.
- Prioritize High-Impact Integrations: Start with CRM-to-sales engagement or marketing-to-CRM. Focus on workflows that directly impact pipeline velocity.
- Establish Data Quality Standards: Set field mapping rules, deduplication logic, and enrichment triggers. Build validation workflows to catch errors early.
- Test in Sandbox: Run pilot integrations with a subset of data. Validate field mapping, test error handling, and measure sync speed.
- Roll Out Incrementally: Deploy to one team or region first. Gather feedback, refine workflows, then expand organization-wide.
- Monitor and Optimize: Track sync errors, data quality metrics, and user adoption. Continuously tune based on performance data.
The best integration projects include change management from day one. Train teams on new workflows, create documentation, and designate integration champions to support adoption.
Measuring ROI: How to Track Integration Impact
B2B software integration should deliver measurable business outcomes. Track these metrics:
| Metric Category | What to Measure | Target Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Time Savings | Hours saved on manual data entry per rep per week | Significant reduction in non-selling activities |
| Data Quality | Percentage of records with complete, accurate data | Measurable improvement in contact completeness |
| Pipeline Velocity | Days to move leads from MQL to SQL to Opportunity | Faster progression through sales stages |
| Tech Stack Costs | Total software spend before and after consolidation | Substantial reduction in overlapping tool costs |
| User Adoption | Percentage of reps actively using integrated workflows | Widespread team engagement with new systems |
The most important metric is whether integration enables your team to execute their B2B buyer journey strategy more effectively. If reps can't act on integrated data, the integration failed regardless of technical success.
Wasting time syncing data between tools? Apollo's API connects your entire sales stack in one unified platform.
Security, Compliance, and Data Governance
B2B software integration introduces security and compliance risks that must be managed proactively:
- Data Access Controls: Implement role-based permissions so users only see data relevant to their function. Audit who can create, read, update, and delete records.
- Encryption in Transit and at Rest: Ensure all data flowing between systems uses TLS 1.2+ encryption. Verify that integrated platforms encrypt stored data.
- Compliance Frameworks: Map integration flows to GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations. Document data retention policies and deletion procedures.
- Change Management: Require approval workflows for integration changes that affect sensitive data or critical business processes.
- Incident Response: Establish procedures for handling sync errors, data breaches, or integration failures. Define escalation paths and recovery processes.
Work with legal and security teams early in the integration planning process. Compliance isn't a checkbox—it's an ongoing governance requirement that affects architecture decisions.
The Case for Platform Consolidation
The fastest-growing B2B teams are moving away from best-of-breed integration nightmares toward unified platforms. Instead of connecting 8-10 separate tools, they consolidate prospecting, enrichment, engagement, and analytics into one workspace.
This approach delivers multiple benefits: fewer integration points to maintain, single source of truth for data governance, unified user experience for reps, and substantial cost savings versus licensing multiple tools.
Modern platforms like Apollo combine B2B data intelligence, sales engagement, and AI-powered automation in one system. This eliminates the need to integrate separate prospecting, enrichment, and outreach tools—cutting complexity and cost while improving data quality.
Start Building Your Integration Strategy
B2B software integration is a strategic imperative, not a technical project. The companies winning in 2026 have moved beyond fragmented tech stacks to unified platforms that enable AI-driven workflows, maintain data quality, and deliver measurable ROI.
Start by auditing your current integrations, identifying high-impact workflow improvements, and evaluating whether consolidation makes more sense than connecting more tools. The goal isn't perfect integration—it's enabling your revenue team to execute faster with better data.
Ready to cut your tech stack and unify your go-to-market workflows? Start prospecting with Apollo's all-in-one platform.
Prove Apollo's ROI In Your First 30 Days
Budget approval stuck on unclear metrics? Apollo tracks every touchpoint from first contact to closed deal. Built-In increased win rates 10% and ACV 10% with measurable pipeline impact.
Start Free with Apollo →
Cam Thompson
Search & Paid | Apollo.io Insights
Cameron Thompson leads paid acquisition at Apollo.io, where he’s focused on scaling B2B growth through paid search, social, and performance marketing. With past roles at Novo, Greenlight, and Kabbage, he’s been in the trenches building growth engines that actually drive results. Outside the ad platforms, you’ll find him geeking out over conversion rates, Atlanta eats, and dad jokes.
Don't miss these
Sales
Inbound vs Outbound Marketing: Which Strategy Wins?
Sales
What Is a Sales Funnel? The Non-Linear Revenue Framework for 2026
Sales
What Is a Go-to-Market Strategy? The Data-Driven Blueprint That Actually Works
See Apollo in action
We'd love to show how Apollo can help you sell better.
By submitting this form, you will receive information, tips, and promotions from Apollo. To learn more, see our Privacy Statement.
4.7/5 based on 9,015 reviews
